Increase Your Order Value With Smart Upsells
Personalize product recommendations, customize upsell offers, increase AOV, and boost sales with our all-in-one WooCommerce Upsell plugin.

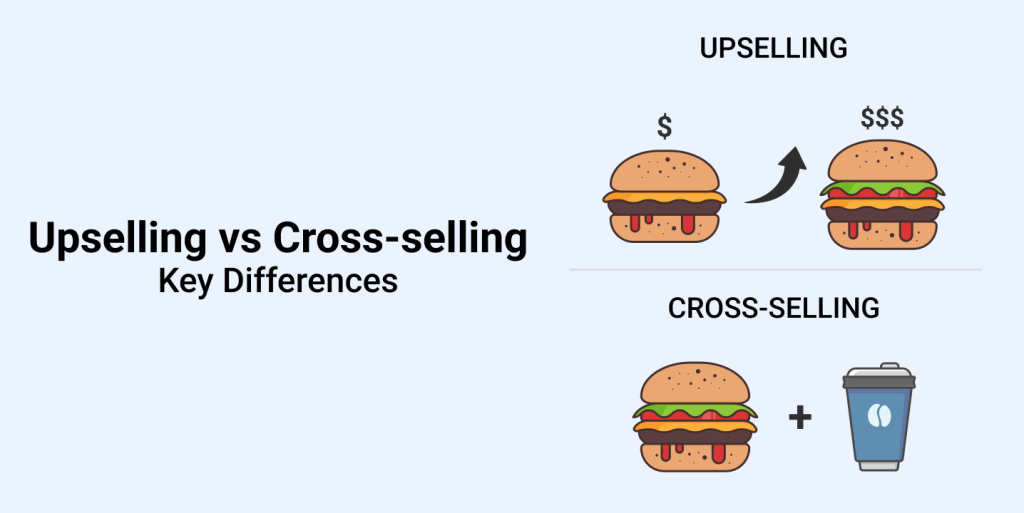
Confused about cross selling vs upselling? While they both may sound similar, they play very different roles in sales.
Understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling effectively increases your store’s revenue. But what exactly are upselling and cross-selling? How do they differ, and more importantly, how can you use them effectively?
In this blog, we’ll break down the differences between Upselling vs cross selling, explain how each can benefit your business, and provide tips on how to implement them effectively. Let’s get started.
Increase your store revenue without extra marketing spend by offering cross-sell products using the UpsellWP plugin.
Cross selling vs Upselling has always been a point of debate and confusion for many store owners. Here’s a clear explanation on its differences and commonalities between them.
Cross selling is a sales technique where sellers recommend additional or related products to an existing customer.
An example of cross selling would be, imagine you’re ordering a burger at a restaurant. If the server suggests adding fries and a coffee to complete your meal, that’s cross-selling. They are offering you products that complement your original choice.
More Info: How to Create Cross-sells in WooCommerce
Upselling is a sales technique used by sellers to encourage customers to buy a more expensive version of an item, upgrade, or add-on in an attempt to make a more profitable sale.
An example of upselling would be if you are buying a coffee, upselling would occur if the seller asks, “Would you like to make it large for an extra dollar?” You’re still getting your coffee, but the seller is trying to increase your spend by offering a larger size.
More Info: A Guide to Upsell Products in WooCommerce
| Suggesting a memory card and lens cleaning kit as add-ons to the main product, the camera. | Upselling | Cross-Selling |
| Definition | Encouraging customers to buy a higher-end, more expensive version of a selected item. | Suggesting related or complementary products that go along with the item being purchased. |
| Objective | Increase the order value by selling a more premium version of the product. | Expand the order size by adding more products to the initial purchase. |
| Timing | Often presented during checkout as an order bump or through follow-up offers after initial purchase. | Usually occurs during the customers’ shopping process, suggesting related items before finalizing their purchase. |
| Sales Technique | Often relies on showcasing the superior features and benefits of a premium product. | Relies on understanding customer needs and suggesting additional products that meet those needs. |
| Examples | Suggesting a basic model camera to a premium model with more features. | Suggesting memory card, and lens cleaning kit as add-ons to the main product, camera. |
Despite serving different purposes, cross selling vs upselling shares several strategic similarities. Here’s a list of it.
Also Read: How to time your Upsell offers
Also Read: How to Perform A/B Testing in Checkout Upsell?
In WooCommerce and eCommerce, tools like UpsellWP make cross selling simple by letting store owners choose a trigger product and pair it with relevant add-ons that appear at the right moment, without interrupting the buyer experience. These cross-sell products can be placed on product pages, carts, or even post-purchase.
This part delves into how to spot and take advantage of cross-sell opportunities. Learn the tactics for making these cross sell offers naturally during the buying process.
Using these tips, you can decide when it’s best to upsell or cross-sell, making sure your suggestions are helpful and likely to lead to more sales for your store.
Some things you need to be aware of while doing cross-selling in your eCommerce store are listed below.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| ✔ Focus on contextual relevance Cross-sell recommendations should align with the customer’s immediate purchase intent. Use product dependency logic (e.g., camera → memory card) and avoid generic “popular items.” Highly contextual offers convert up to 3–5× better and feel like part of the buying experience, not an interruption. | ✘ Don’t interrupt the checkout flow Avoid full-page popups or complicated bundles during checkout. Anything that introduces cognitive load at a high-intent stage risks abandoned carts—one of the most costly mistakes in cross-selling. |
| ✔ Prioritize “low-friction” add-ons Successful cross-sells typically fall under 10–20% of the primary product’s price. Lower-cost, accessory-type items reduce decision fatigue and encourage impulse acceptance—especially on cart and checkout pages. | ✘ Don’t recommend products with unclear value connection If the shopper has to think about why the item is being suggested, the cross-sell fails. Avoid weak associations like “laptop → office chair.” Every offer should have a direct functional or experiential tie-in. |
| ✔ Use behavioral triggers to increase uptake Incorporate elements like: 1. Social proof: “Bought together by 68% of customers.” 2. Utility cues: “Protect your device with…” 3. Loss aversion: “Don’t miss out on extended warranty coverage.” These triggers subtly justify the additional purchase without pushing hard. | ✘ Don’t recycle the same offers across every stage Showing identical cross-sells on product, cart, and checkout pages creates “banner blindness.” Instead, sequence offers intelligently—for example, accessory cross-sells on product pages, warranty/add-ons at checkout. |
| ✔ A/B test offer placement and sequencing Cross-sells on the product page serve discovery, while cart/checkout cross-sells serve conversion. Test different entry points, especially in WooCommerce environments where customer intent changes quickly. | ✘ Don’t overwhelm users with multiple offers Presenting more than 1–3 cross-sell options leads to decision paralysis. Expert setups restrict recommendations to a tightly curated set tied to the original product. |
| ✔ Personalize recommendations with real user data Leverage browsing history, past purchases, or cart behavior to tailor suggestions. Tools like UpsellWP let you create dynamic rules that prevent repetitive or irrelevant offers. | ✘ Don’t push post-purchase items that complicate fulfillment Avoid suggesting items with different shipping classes or processing requirements on post-purchase pages. Keep one-click upsells limited to items that can ship together or be fulfilled without added cost. |
Some examples of cross selling used by major brands are given below.
1. Sephora cross sell example: When a customer looks for a lipstick, Sephora suggests related cross sell products like micellar water, lip liner to increase the customer’s purchase value.
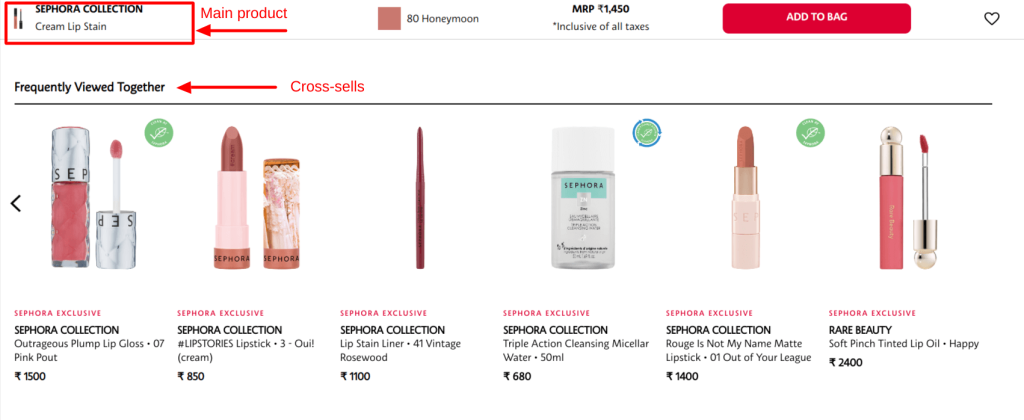
2. FlipKart cross selling example: When a customer is shopping for a pair of shoes, cross selling would be suggesting relevant/additional products like shirts or sandals that go well with the main product.
Upselling encourages customers to choose a better, higher-value version of the same product they’re considering. With UpsellWP, you can automate premium product recommendations on product pages, helping customers make smarter choices while increasing your store’s revenue with no extra efforts.
Increase your profit per customer with high-value upgrades by upselling relevant products using the UpsellWP plugin
Here, we look at the best times to use upselling. Understand the signs that a customer is ready for an upgrade and how to make your upsell offer at just the right moment.
Some of the points to keep in mind while doing upselling are,
| ✘ Don’t attempt upsells too late in the journey. Showing an upsell at checkout is a common mistake. At this stage, users want to complete the purchase, not reevaluate product choices. Reserve checkout for cross-sells instead. | Don’ts |
| ✔ Offer meaningful value upgrades – not just higher prices A strategic upsell highlights tangible improvements such as more storage, faster processing, premium materials, or extended features. The customer should immediately understand why the higher-priced alternative is better for them. Clear value = higher acceptance. | ✘ Don’t push upsells that exceed 30–50% of the original product price High-price jumps introduce friction, increase scrutiny, and feel salesy. The upsell must feel like a reasonable upgrade, not a bait-and-switch. |
| ✔ Use tier-based comparisons to anchor value Upselling is more effective when customers can see the difference between the base product and premium alternatives. Use: 1. Feature comparison tables 2. “Most popular” labels 3. Price anchoring (e.g., showing the mid-tier as the best value) This reduces cognitive effort and guides buyers toward the optimal upgrade. | ✘ Don’t attempt upsells too late in the journey Showing an upsell at checkout is a common mistake. At this stage, users want to complete the purchase—not reevaluate product choices. Reserve checkout for cross-sells instead. |
| ✔ Present upsells early—before the customer commits mentally Upsells work best on product pages, not the cart or checkout. Once a customer has emotionally committed to a product, their willingness to consider alternatives decreases drastically. | ✘ Don’t upsell when the user’s goal is narrow or urgent If the customer is buying a product to solve a specific, immediate need, additional complexity can become an obstacle. Not every buyer is a candidate for an upsell, and forcing one can harm conversion rates. |
| ✔ Limit upsells to a single, best-fit option Unlike cross-selling, where offering 2–3 items is acceptable, upselling should be hyper-focused. Presenting multiple upgrades reduces clarity and creates analysis paralysis. Your goal is to highlight the best possible next step. | ✘ Don’t rely solely on price-driven upgrades A more expensive version isn’t enough. The perceived value gap must be clear. Avoid upsells that simply say “Premium Version—More Features!” without explaining which features matter. |
| ✔ Use personalization based on real behavioral indicators Upsell acceptance increases when based on: 1. Past spending patterns 2. Browsing depth (e.g., viewing premium tiers multiple times) 3. Cart value and category preferences UpsellWP rules can dynamically tailor premium recommendations based on this data. | ✘ Don’t repeat the same upsell across every product Lazy upsell strategy dilutes trust. Each upsell should be tightly tied to the core product. Broad, generic recommendations feel automated and reduce relevance—one of the biggest killers of upsell conversions. |
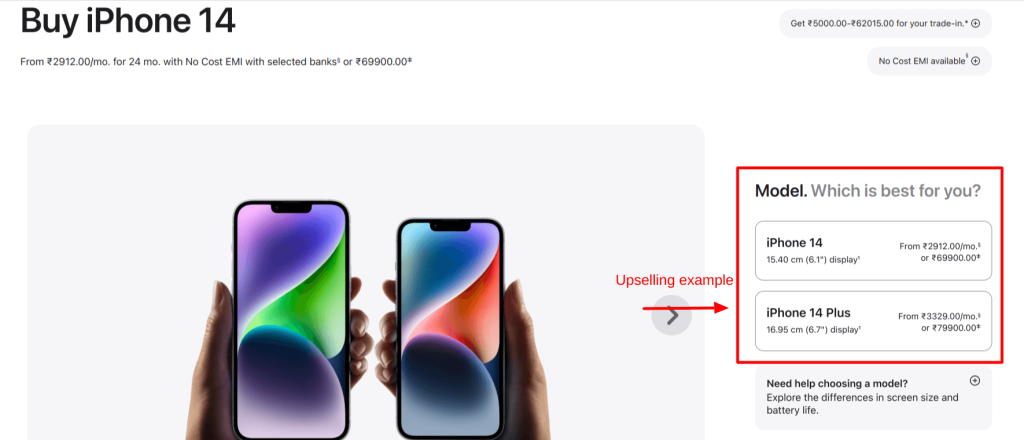
1. Apple Upselling example: When shopping for an iPhone on Apple’s website, customers are often recommended a premium version of the iPhone to increase their purchase value.
2. GoPro upselling example: When a customer looks at a basic model, GoPro’s website suggests considering a more advanced version that captures superior footage.
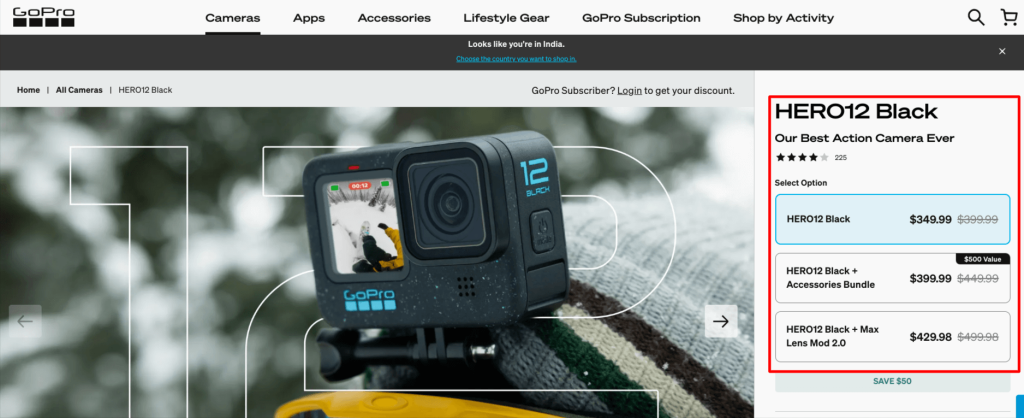
There’s no clear winner to Cross selling vs Upselling debate. Upselling focuses on upgrading the single product the customer intends to buy, whereas cross selling aims to increase the total number of products purchased.
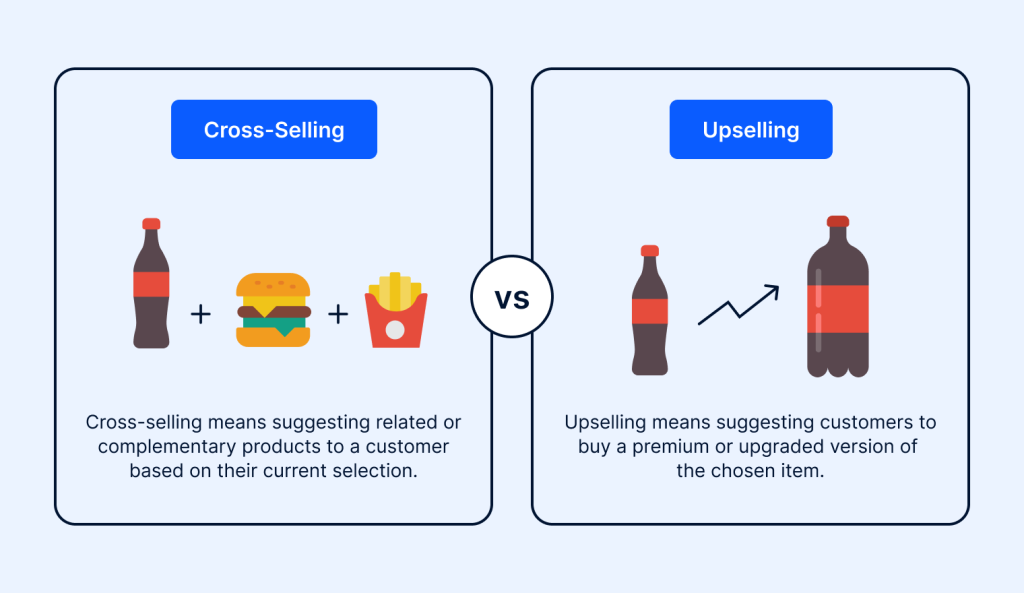
Both upselling vs cross selling aim to increase average order value and sales; they do so in different ways. Also, you might wonder, “Should I focus on one more than the other?
Eventually, cross selling vs upselling, it’s not about choosing one over the other; it’s about finding the right balance between them and using both in a correct way.
Now that you know what upsell vs cross sell, let us see how to properly balance cross selling vs upselling. It’s about understanding the customer’s situation and offering products that truly make their shopping better.
After balancing both upsell and cross sell, knowing when to use each method is important for using them effectively.
In this section, we explore where in the shopping process you can effectively put upsell and cross-sell strategies to work.
More Info: How to Add WooCommerce Upsells on Cart Pages and Side Carts
More Info: How to Show the Related Upsell Products on the Thank You Page
Downselling is when you offer a more affordable or simpler version of the product if a customer shows hesitation.
It’s a great way to save a sale instead of losing the customer completely.
Example:
If someone is unsure about buying a $120 premium plan, showing them a $60 basic plan increases the chance they will still complete the purchase.
Bundling groups related products together into a single, value-focused package.
This helps customers feel like they’re getting everything they need in one go, without being separately “sold to.”
Example:
Instead of cross-selling skincare items one by one, offer a “Complete Skincare Starter Kit.”
Instead of recommending extra items during checkout, you can motivate customers to come back with points, cashback, or rewards.
This doesn’t increase order value instantly, but boosts long-term loyalty and repeat purchases.
Example:
“Earn 100 points for every purchase and redeem them for discounts.”
Subscriptions help you secure recurring orders without asking customers to buy more at checkout.
This works especially well for products people need regularly.
Example:
“Subscribe & Save 15%” for pet food, vitamins, or coffee.
These are simple motivators that encourage customers to add a little more to reach a reward or unlock savings.
Example:
“Spend $75 to get free shipping” or “Add $10 more to get a gift.”
Shoppers naturally increase their order value without you having to recommend specific products.
Product quizzes and recommendation tools help customers choose the right product from the start.
This reduces confusion and minimizes the need for upsells or cross-sells later.
Example:
A quiz that helps customers pick the best laptop based on their usage (gaming, travel, office).
Instead of manually suggesting products, you can show what other customers commonly buy.
This creates trust and encourages people to choose popular combinations or bundles.
Example:
“Best-Selling Kits”
“Customers’ Favorites This Week”
These naturally guide shoppers toward higher-value purchases without feeling like a sales push.
Increase your store’s conversion rates by showing hyper-relevant product recommendations to your customers that feel tailor-made using the UpsellWP plugin.
Cross selling vs Upselling really depends on your own business situation—like what kinds of products you sell, who your customers are, and the type of shopping experience you want to give. By knowing how each strategy works and using it smartly, you can increase your sales while making your customers loyal.
Mastering cross selling vs upselling also involves creating a buying journey that feels genuinely personal and helpful to your customers. With the right tools like UpsellWP, you aren’t just increasing order value, but building a brand that customers trust and recommend.
Best Guides for Your WooCommerce Store:
Here is the difference between these two suggestive selling te.chniques. Upselling involves convincing customers to purchase a more expensive, upgraded, or premium version of a chosen item. Cross-selling, on the other hand, encourages buying additional products that complement the original item.
Cross-selling example: A phone case when buying a smartphone; a hair conditioner with shampoo.
Upselling example: Offering a larger size of a coffee; upgrading a flight to premium economy.
The four stages of upselling include identifying the opportunity, understanding the customer’s needs, presenting the benefits of an upgraded product, and closing the sale by making the upsell offer.
Cross-selling involves offering additional products that complement or enhance the main purchase. For example, suggesting a protective screen protector and earphones when a customer buys a new smartphone.
Cross selling can overwhelm customers if the recommendations aren’t relevant, leading to decision fatigue or cart abandonment. Poorly targeted cross-sells may also feel pushy and reduce trust in the buying experience.
The 25% rule suggests that cross-sell products should typically cost no more than 25% of the main product’s price. This keeps the offer low-risk, easier to accept, and better aligned with impulse-buy behavior.
Cross-selling increases average order value, improves the customer experience by offering useful add-ons, and increases revenue without acquiring new customers. It also helps shoppers discover complementary products they may have otherwise missed.